モータースポーツを支えるアスレチックトレーナーを目指してアメリカへ留学しています。Skeletal systemについて知っておきたいキーワードを独断と偏見で選びました。冬休み中に随時更新予定。(1st 12/14 2nd 12/18)
7.1 Skeletal anatomy overview
- Tubercle
- Process
7.2 Axial skeleton
- Skull -calvaria 頭頂骨
- Superior view of the skull
- parietal bones
- sagittal suture
- frontal bone
- coronal suture
- Posterior
- occipital bone
- lamboid suture
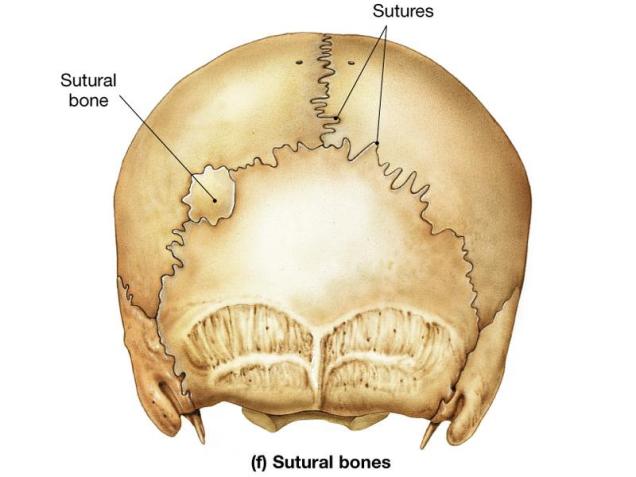
- sutural bone 縫合骨
- Lateral
- squamous suture 鱗状縫合
- External auditory canal (temporal bone)
- mastoid process
- Mastoid air cell 乳突蜂巣 -process is not solid bone but is filled with cavities
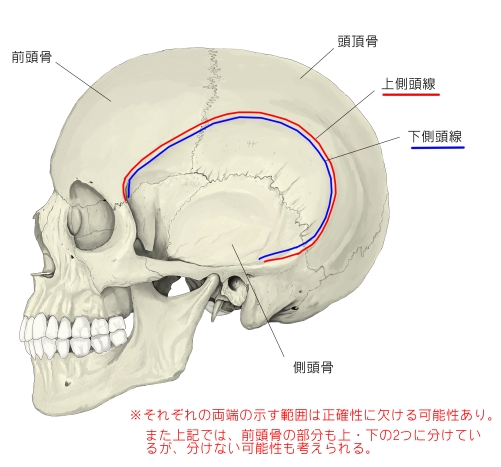
- Temporal lines -attachment points of the temporalis muscle
- Greater wings of the sphenoid bone
- zygomatic bone
- Zygomatic arch
- Maxilla
- Mandible
- body
- ramus
- condyle
- Coronoid process
- Anterior
- nasolacrimal canal
- optic canal 視神経管
- Nasal cavity
- nasal septum
- Nasal conchae : lateral wall of the nasal cavity
- Paranasal sinuses 副鼻腔(ふくびこう 医学用語:ふくびくう 英語:paranasal sinuses)とは、鼻腔に隣接した骨内に作られた空洞であり、ヒトでは前頭洞、篩骨洞、上顎洞、蝶形洞の4つがある。
- Inferior cranial cavity
- Cranial cavity
- Crista galli 鶏冠 the center of the anterior fossa just superior nasal cavity
- Meninges 髄膜 : crista galli is a point of attachment for one of the meninges
- Cribriform plate 多孔の、篩状の of the ethmoid bone
- Olfactory foramina :
- Sella turcica トルコ鞍 : which is occupied by the pituitary gland
- anterior cranial fossa
- middle cranial fossa
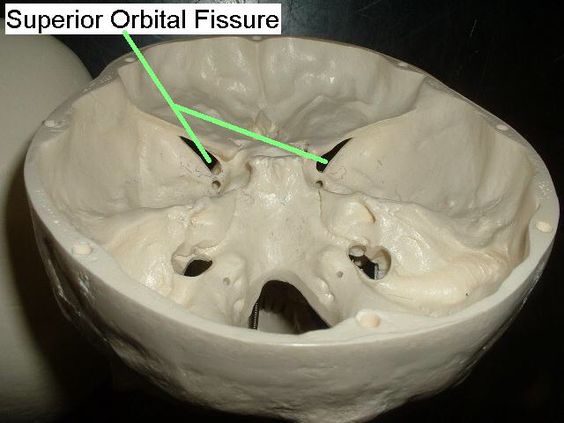
- Superior orbital fissure
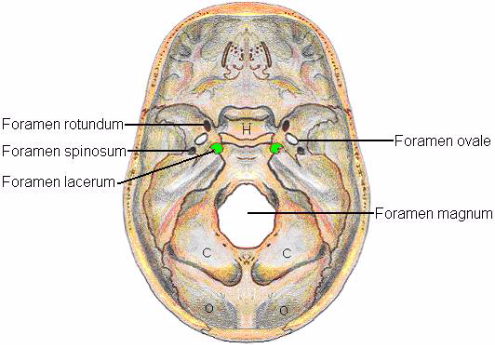
- Foramen rotundum 正円孔(せいえんこう)は蝶形骨にある円形の穴で中頭蓋窩(英語: middle cranial fossa)と翼口蓋窩(英語: pterygopalatine fossa)をつなぐ。
- 上顎神経(Ⅴ2)
- Foramen ovale 卵円孔(らんえんこう)とは、蝶形骨大翼の卵円孔
- 下顎神経(Ⅴ3)
- Foramen spinosum 棘孔
- 中硬膜動脈・静脈
- Posterior cranial fossa
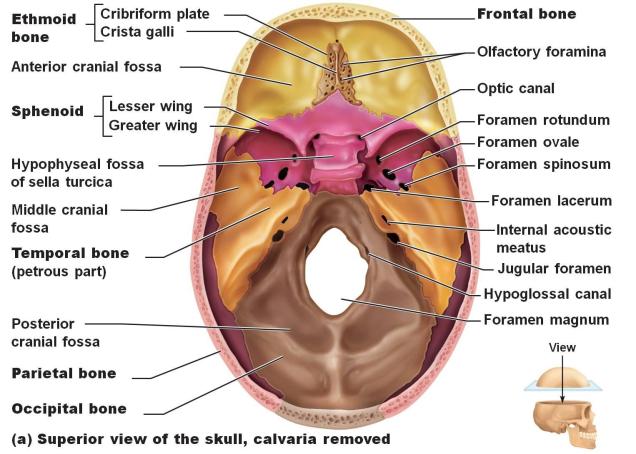
- Foramen lacerum
- 頸動脈
- 交感神経
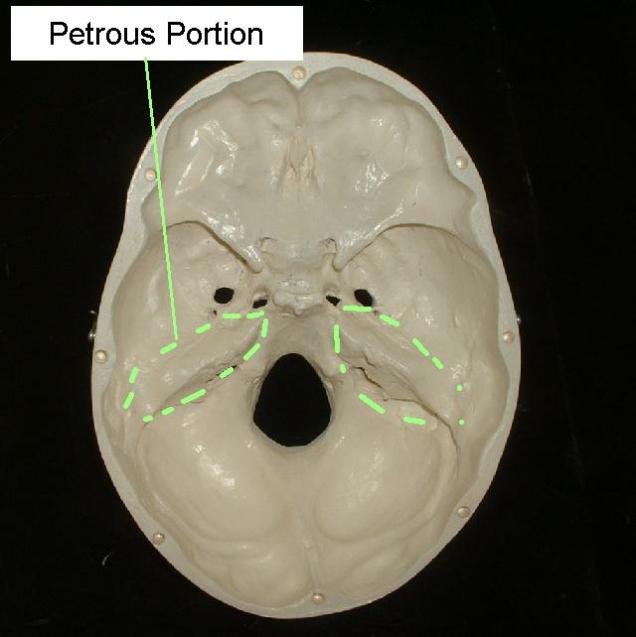
- Petrous portion 側頭骨錐体; 錐体突起
- Foramen magnum : vertebral arteries pass through
- Hypoglossal canal : anterolateral sides of the foramen magnum
- Jugular foramina :
- Internal auditory canal
- Inferior view of the skull
- Occipital condyle
- Carotid canal : internal carotid artery
- Styloid process
- Mandibular fossa : mandible articulates with the rest of the skull
- Medial pterygoid plate 翼状突起の内側板 -内側翼突筋
- Lateral pterygoid plate 翼状突起の外側板 -外側翼突筋(がいそくよくとつきん)とは、人間の咀嚼筋の1つで、下顎を前方あるいは側方に動かす機能を担う随意筋である。
- Vomer
- Hard plate
- Individual bones of the skull
- Auditory ossicles耳小骨: 6 inner ear bones
- 22 separate bones
- Brain case (8)
- Parietal bone
- Parietal bone
- Temporal bones
- Temporal bones
- Frontal
- Occipital
- Sphenoid
- Ethnoid
- Facial bones (14)
- Zygomatic
- Palatine
- Lacrimal
- Nasal
- Inferior nasal concha
- Mandible
- Vomer
- Mastication
- Alveolar process : mandible and maxillae have these process for teeth
- Brain case (8)
- Superior view of the skull
- Hyoid bone
- Vertebral column
- 7 cervical vertebrae
-
- 12 thoracic vertebrae
- 5 lumber vertebrae
- 1 Sacral bone
- 1 coccygeal boneOverview (26 bones)
- General features of the vertebrae
- Body
- Vertebral arch
- Pedicle椎弓根: which is attached to the body
- Lamina椎弓の薄板: joins with the lamina from the opposite side of the arch
- Vertebral foramen
- Vertebral canal 脊柱管
- Transverse process
- Spinous process
- Intervertebral foramina 椎間孔
- Intervertebral notches
- 2 Superior articular process
- 2 Inferior articular process
- Articular facet
- Intervertebral disks
- External annlus fibrous
- Internal nucleus pulposus
- regional differences in vertebrae
- Cervical vertebrae
- Bifid spinous processes ; split spinous process
- Transverse foramen : vertebral arteries
- Atlas : C1
- Axis : C2
- Dens
- Vertebral prominens : spinous process of the seventh vertebra
- Whiplash むちひも、むち打ち
- Thoracis vertebrae
- Lumber vertebrae
- Sacal vertebrae
- alae 翼
- Articular surfaces : which join the scrum to the pelvic bones
- Median sacral crest : 正中仙骨稜
- Sacral hiatus 仙骨管裂孔
- Sacral foramina
- Transverse lines
- Sacral promontory 仙骨岬角 -a landmark that separates the abdominal cavity from the pelvic cavity
- Cervical vertebrae
- Vertebral column
- Rib cage
- Ribs and costal cartilages
- 12 ribs
- 7 true ribs
- 5 false ribs
- 8th, 9th, 10th -vertebrochondral ribs 脊椎肋軟骨の
- 11th, 12th -floating ribs
- Separated ribs
- 2 points of articulation
- Head articulation
- Tubercle articulation
- Neck
- Body
- Angle
- Cervical ribs 頸肋, 頚肋
- 12 ribs
- Sternum
- Manubrium
- Jugular notch
- Sternal angle
- Body
- Xiphoid Process
- Manubrium
- Ribs and costal cartilages
Table は3週目に整理しよう!
7.3 Appendicular skeleton
- Pectoral girdle and upper limb
- Pectoral girdle
- Scapula
- Acromion process -attachment site for clavicle
- Scapular spine : extends from the acromion process
- Supraspintus fossa
- Infraspinatus fossa
- Subscapular fossa
- Coracoid process (meaning shaped like a crow’s beak)
- Glenoid cavity
- Cavicle
- Scapula
- Arm
- Humerus
- Humerus head : articulate with glenoid cavity
- Anatomical neck : immediately distal to the head
- Surgical neck : common fracture site that often requires surgical repair
- Greater tubercle
- Lesser tubercle
- Intertubercular groove
- Deltoid tuberosity
- Capitulum 顎体部; 小頭 very rounded lateral portion of the articular surface of humerus for radius
- Trochlea : 滑車 : articulate with the ulna. somewhat resenbles a spool
- Lateral / medial epicondyle
- Forearm
- Ulna
- Trochlear notch : C-shaped articular surface
- Olecranon process : 肘頭突起 : the larger, posterior process
- Coronoid process 鉤状突起、筋突起 : smaller anterior process
- Head
- Styloid process : to which ligaments of the wrist are attached
- Radius
- Head
- Radial notch of ulna
- Radial tuberosity : is the point at which a major anterior arm muscle, biceps brachii, attaches.
- Ulna
- Wrist
- Carpal bone
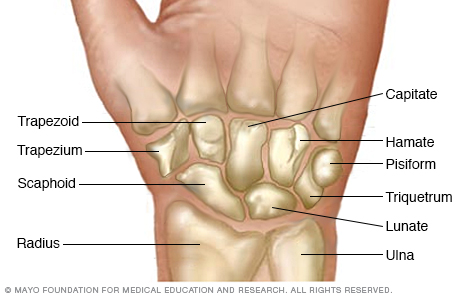
- Proximal row
- Scaphoid : boat shaped
- Lunate : moon shaped
- Triquetrm : three cornered
- Pisiform : 豆状骨
- Distal row
- Hamate : which has a hooked process on its palmer side
- capitate :有頭骨 head shaped
- Trapezoid :小菱形骨
- Trapezium : 大菱形骨
-
So Long Top Part, Here Comes The Thumb : Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetum, Pisiform, Hamate, Capitate, Trapezoid, Trapezium
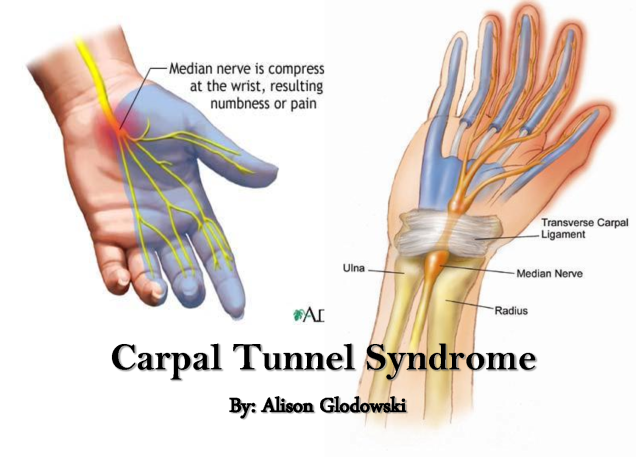
- Carpal tunnel
- Hand
- Metacarpal bones
- Digits
- Sesamoid bone
- Pectoral girdle
- Pelvic girdle and lower limb
- Pelvic girdle
- Hipbones
- Ilium
-
- Ischium
- Pubis
- Pelvic girdle
- Obturator foramen
- Acetabulum
- Iliac crest
- Anterior superior iliac spine
- Posterior superior iliac spine
- Greater sciatic notch : on posterior side of the ilium, just inferior to the PIIS. The sciatic nerve pass through.
- Auricle surface : articulates with sacrum -sacroiliac joint
- Iliac fossa
- Ischial tuberosity : posterior thigh muscles
- Pubic crest :
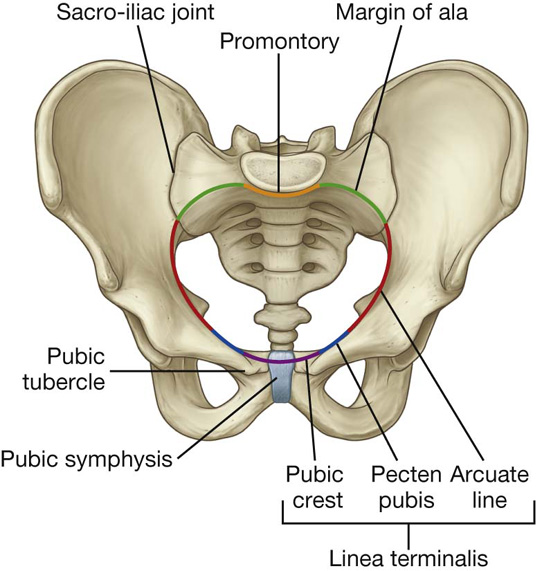
- Pubic tubercle : inguinal ligament attaches.
- Pubic symphysis
- True pelvis -pelvic inlet
- False pelvis -pelvic outlet
- Comparison of the male pelvis and the female pelvis
- cesarean section 帝王切開術
- Hipbones
- Thigh
- Femur
- head
- Neck
- Greater trochanter
- Lesser trochanter
- Medial / Lateral condyle : smooth, rounded surfaces that articulate with the tibia
- Medial / Lateral epicondyle
- Adductor tubercle
- Patella
- Leg
- Tibia
- Tibial tuberosity
- Anterior crest : forms shin
- Medial / Lateral condyle : articulate with the condyles of the femur
- Intercondylar eminence : a ridge between the two articular surfaces
- Medial malleolus
- Fibula
- Lateral malleolus
- Tibia
- Foot
- Tarsal bones
- Talus: articulate with the tibia and fibula
- Calcaneus
- Navicular
- Cuneiforms
- Lateral
- Medial
- Intermediate
- Cuboid -4th, 5th
- Metatarsal bones / phalanges
- Arches
- Medial longitudinal arch
- Lateral longitudinal arch
- Transverse arch
- Pelvic girdle
- Cleft palate or lip
- A cleft lip alone, or both cleft and lip, occurs once in every 1000 births and is more common in males.
- A cleft palate only occurs once in every 2000 births and more common in females
- Herniated intervertebral disk
- A herniated disk results when the annulus fibrosus breaks or balloons, releasing all or part of the nucleus pulposus 髄核
- The inferior lumbar and inferior cervical intervertebral disks are the most common disks to become herniated
- because the vertebral column has a lot of mobility in these areas
- Treatment
- laminectomy 椎弓切除術、椎弓切除
- is the removal of vertebral lamina, or vertebral arch
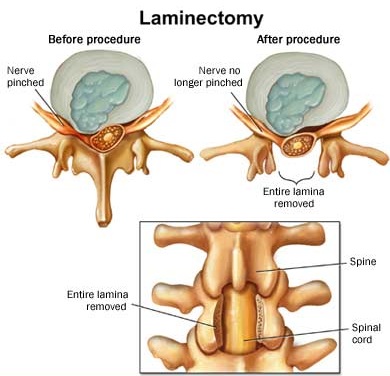
- is the removal of vertebral lamina, or vertebral arch
- hemilaminectomy : 片側椎弓切除
- is the removal of a portion of a vertebral lamina
- Fenestration 窓割り、(内耳)開窓術
- involves removal of the nucleus pulposus髄核, leaving the annulus fibrosus線維輪 intact
- In extreme cases, the entire damaged disk is removed and a metal cage is inserted into the space previously occupied by the disk.
- Red bone marrow stem cells harvested from the hip are then injected into the space to allow for new bone growth.
- laminectomy 椎弓切除術、椎弓切除
- Gluteal injection
- gluteal muscles are a common site for intramuscular injections
- Gluteal injections are made in the superolateral region of the hip because a large nerve (the sciatic nerve) lies deep to the other gluteal regions
- Tha land marks for such an injection are the anterior superior iliac spine and the tubercle of the iliac crest, which lies about 1/3 of the way along the iliac crest from anterior to posterior.
- Patellar defects
- The patella normally tracks in the patellar groove on the anterodistal end of the femur
- As a young woman’s hips widen during puberty, the angles at the joints between the hips and the tibia may change considerably.
- As the knee becomes located more medially relative to the hip, the patella may be forced to track more laterally than normal.This lateral tracking may result in pain in the knees of physically active women.
- A broken hip
- Femoral neck fracture are among the most common injuries resulting in morbidity (disease) and mortality (death) in older adults
- 4% of women over age 85 experience femoral neck fractures each year.
- Despite treatment with anticoaglants and antibiotics, about 5% of patients with femoral neck fractures develop deep vein thronbosis (blood clot)
- 5% develop wound infections
- Hostital mortality is 1-7%
- 20% of patients die within 3 months of the fracture
- Only about 25% of victims ever fully recover from the injury.
- Fractures of the Malleoli
- When the foot is forcefully everted, the medial malleolus moves inferiorly toward the ground or the floor and the talus slides laterally, forcing the medial and lateral malleoli to separate.
- the ligament holding the medial malleolus to the tarsal bones is stronger than the bones it connects, and often it does not tear as the bones separate because of eversion
- Pott fracture : as the talus slides laterally, the force can shear off the lateral malleolus or, more commonly, cause the fibula to break superior to the lateral malleolus.
- Inversion sprain : because the ligament holding the medial malleolus to the tarsal bones is weaker than the bones it connects, inversion of the foot causes a sprain in which ligaments are damaged.